Business structures — and their tax implications
When starting a company, selecting a suitable business structure that aligns with your needs and vision is important, as it defines who owns and operates the business in focus. The taxation conditions differ for each structure type, making it crucial to understand the most beneficial business structure. Choosing the right business structure will also position you positively for taxation season, assisting you and your business with; liabilities, taxes, and paperwork.

There are four types of business structures with associated tax implications!
#1- Sole Trader
The simplest business structure with a single company owner. All the decisions are made by them, and they will be responsible for any liabilities, such as debts and losses. As a business owner, you can employ other workers. However, you cannot name yourself as an employee.
Tax implications-
- When taxes are filed, they are due under the owner’s individual tax file number. Therefore, a different tax file number (TFN) is not required.
- The tax rate will be the same as that of individual taxpayers. However, you may be able to receive the small business tax offset.
- If your annual turnover is $75,000 or more, you must register for GST. GST registration is also needed if you provide taxi services or wish to claim fuel tax credits.
To apply for a small business tax offset, you must be carrying on a small business as a sole trader or have a share of net small business income from a partnership or trust.
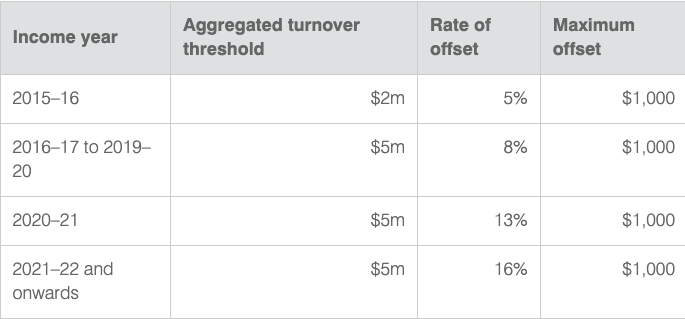
For more information on small business and tax offset and to see if you are eligible, visit the Australian Taxation Office https://www.ato.gov.au/business/income-and-deductions-for-business/in-detail/small-business-income-tax-offset/?anchor=Eligibility#Eligibility
#2- Partnership
A group or association of people running a business. Although having a written agreement can help define how the company is run and the division of profits or losses, it is not required.
Tax implications-
- A TFN is required, and each partner will pay their share of the profit tax.
- The tax rate is that of individual taxpayers. You may get the small business tax offset.
- If your annual turnover is $75,000 or more, you must register for GST.

#3- Company
A company is an entity owned by shareholders and run by directors. A company’s assets and income should not be used for personal benefits, or you will have tax consequences.
Tax implications-
- You will require a new TFN to file taxes as a company.
- The tax rate will be according to the company.
- If your annual turnover is $75,000 or more, you must register for GST.
#4- Trust
The business is handed over to a trustee (a legal third party) to run and control it. A trustee can be a company or an individual, and a formal and legal agreement must be in place.
Tax implications-
- The business tax and rates depend on the wording of the deed and if the income earned is distributed to the beneficiaries.
- You will require a new TFN to file taxes as a company.
- If your annual turnover is $75,000 or more, you must register for GST.
About Sphere Accountants & Advisors-
If you are seeking advice on protecting your assets, your search ends with Sphere Accountants and Advisors. Through working with Sphere Accountants and Advisors, we consider the complete picture and continually look for ways to improve your financial situation to create, protect and grow your wealth. We apply this approach whether you come as an individual or a business. With a breadth of expertise spanning all aspects of taxation, accounting, financial planning and more, we can offer a complete solution for all your financial needs. Visit our website, call us at (03) 8899 6399, or email us for more details.



